PEG Ratio
Table of Contents
Understanding the PEG Ratio Filter
The Price/Earnings to Growth (PEG) ratio is a valuation metric used to assess the relationship between the price of a stock, its earnings per share (EPS), and the company's expected growth rate. Unlike traditional P/E ratios, which focus solely on current earnings, the PEG ratio incorporates the company's projected earnings growth into its valuation. The PEG ratio provides a forward-looking measure of a stock's valuation relative to its expected earnings growth over the next five years.
Calculation: The formula for calculating the PEG ratio is: P/E Ratio / Projected Earnings Growth Rate.
Interpretation: A PEG ratio of 1 indicates that the stock is fairly valued relative to its earnings growth rate. A PEG ratio below 1 may suggest that the stock is undervalued, while a PEG ratio above 1 may indicate overvaluation. A lower PEG ratio suggests that investors are paying less for each unit of expected earnings growth, making the stock potentially more attractive from a valuation perspective. The PEG ratio provides a more comprehensive assessment of a stock's valuation by considering both its earnings and growth prospects.
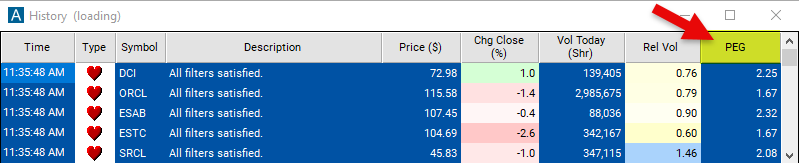
PEG Ratio Filter Settings
Configuring the "PEG Ratio" filter is simple and can be done within the Window Specific Filters Tab of the Configuration Window in your Alert/Top List Window.
Here's how to set up the filter in your configuration window:
- Set the minimum value to 1 to see only stocks in which investors are paying more for each unit of expected earnings growth.
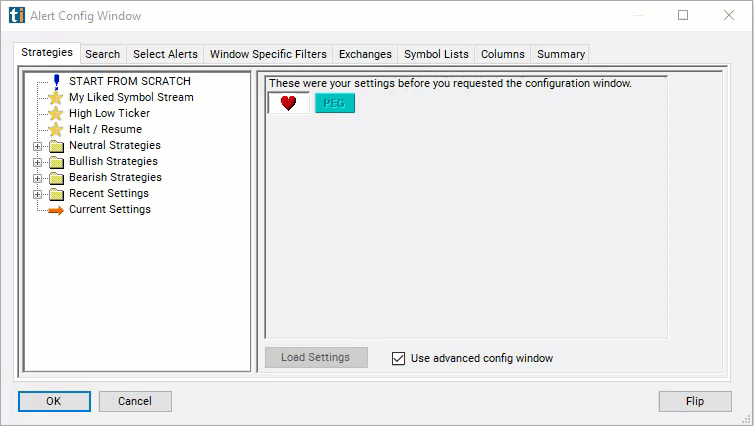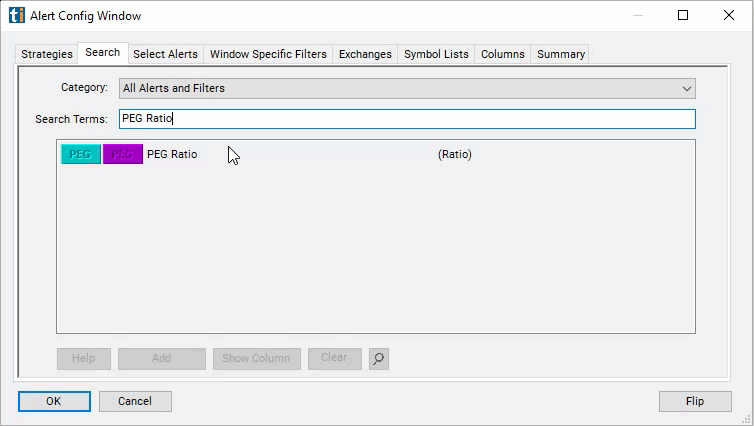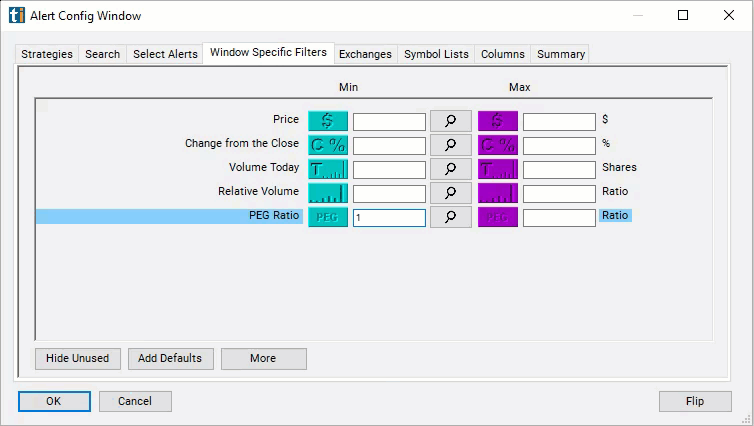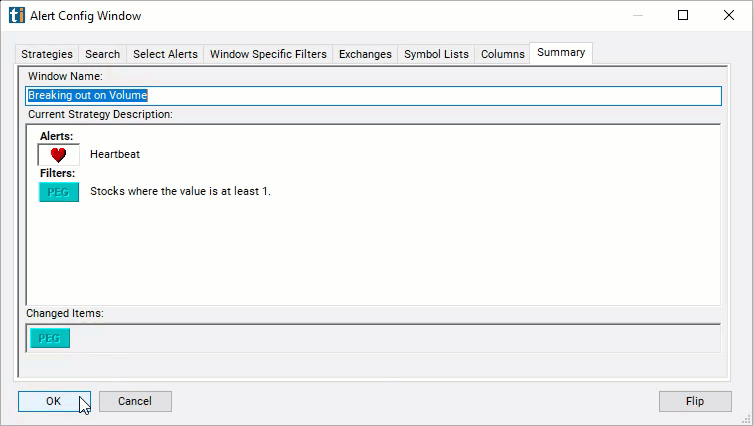
Using the PEG Ratio Filter
The "PEG Ratio" filter can be used in various trading strategies, including:
PEG Ratio Screening: Screen for stocks with PEG ratios below 1, indicating potential undervaluation relative to their earnings growth prospects. Focus on stocks with strong fundamentals, positive earnings growth expectations, and reasonable valuations based on their PEG ratios.
Relative Valuation: Compare the PEG ratios of stocks within the same industry or sector to identify relative valuation disparities. Take long positions in stocks with lower PEG ratios compared to their peers, anticipating potential price appreciation driven by reversion to the mean or market recognition of undervaluation.
Growth Investing: Look for stocks with PEG ratios below 1 that exhibit strong earnings growth potential and positive momentum. Take long positions in growth stocks with attractive PEG ratios, expecting continued earnings expansion and potential capital appreciation.
FAQs
What does the PEG ratio indicate?
- The PEG ratio provides a comprehensive measure of a stock's valuation relative to its earnings growth prospects. It combines the Price/Earnings (P/E) ratio with the expected earnings growth rate to assess whether a stock is overvalued, undervalued, or fairly valued based on its growth potential.
How is the PEG ratio calculated?
- The PEG ratio is calculated by dividing the Price/Earnings (P/E) ratio by the projected earnings growth rate. The formula is: PEG Ratio = P/E Ratio / Projected Earnings Growth Rate. The projected earnings growth rate is typically based on analysts' forecasts or the company's own guidance.
Interpreting High/Low PEG ratios:
- A high PEG ratio may indicate that the stock is overvalued relative to its earnings growth prospects. Conversely, a low PEG ratio suggests potential undervaluation. However, investors should consider other factors such as risk, industry dynamics, and market conditions when interpreting PEG ratios.
Filter Info for PEG Ratio [PEG]
- description = PEG Ratio
- keywords = Fundamentals Changes Daily
- units = Ratio
- format = 2
- toplistable = 1
- parent_code =





